Credits: Stability.ai
Table of Contents
In an era of rapid technological advancement, the life science manufacturing sector stands at the cusp of a transformative revolution. Service as Software (SaaS) is emerging as a game-changing paradigm, promising to reshape the landscape of pharmaceutical and biotechnology production.
This article explores the compelling case for SaaS adoption in life science manufacturing, highlighting its potential to drive innovation, enhance efficiency, and ensure regulatory compliance.
The SaaS Revolution in Life Sciences
SaaS is more than just a technological trend; it represents a fundamental shift in how life science companies approach their manufacturing processes. By leveraging cloud-based software solutions, organizations can transform traditional service-oriented workflows into streamlined, software-driven operations.
From Service-Dominant to Software-Dominant Workflows
The transition to SaaS in life science manufacturing follows a progressive path:
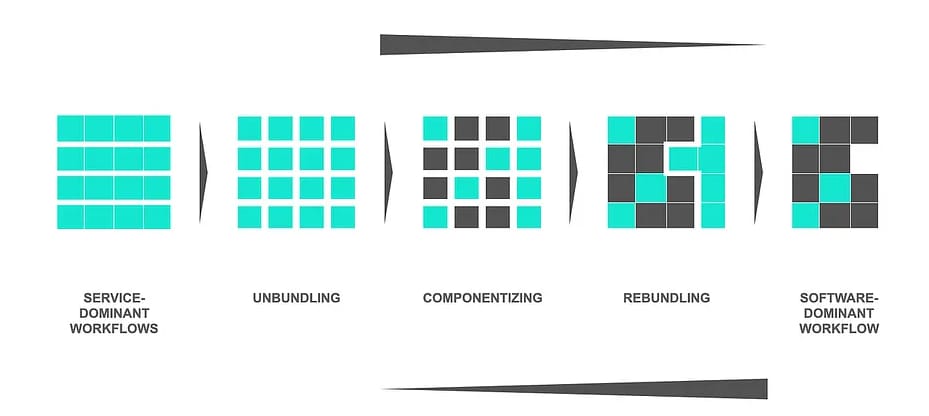
Service-Dominant Workflow
Initially, manufacturing processes heavily rely on human input and decision-making.

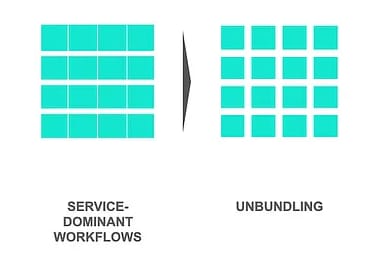
Unbundling
AI technologies begin to break down individual tasks, enabling automation of repetitive processes.
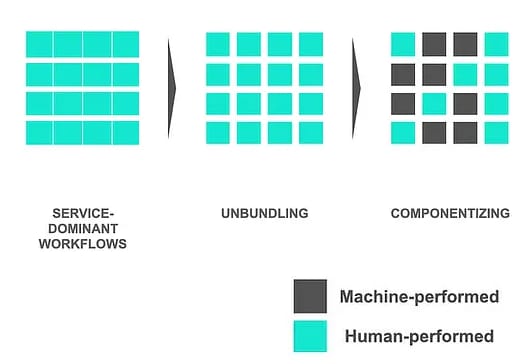
Componentizing
Tasks are segmented into modular components, improving scalability and reusability.
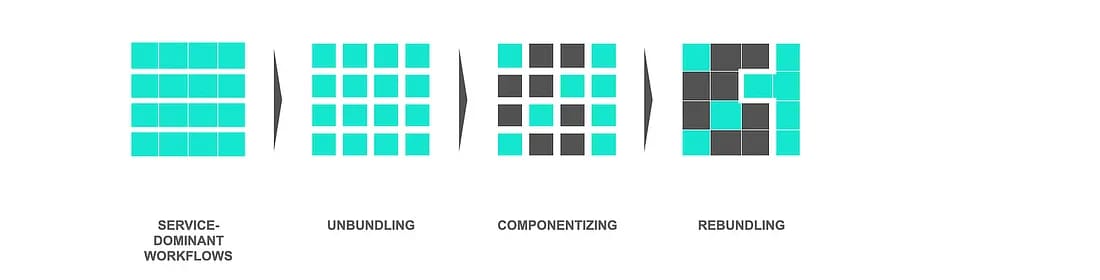
Rebundling
Organizations restructure workflows, creating more efficient operations that harness AI capabilities.
Software-Dominant Workflow
The final stage where software solutions manage most tasks, allowing human employees to focus on strategic initiatives and complex problem-solving.
Key Benefits of SaaS in Life Science Manufacturing
Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
SaaS solutions streamline manufacturing processes by automating routine tasks and providing real-time data analytics. This leads to:
Reduced production times
Minimized human errors
Optimized resource allocation
Improved Quality Control
AI-powered SaaS platforms can:
Detect anomalies in real-time
Predict potential quality issues before they occur
Ensure consistent product quality across batches
Regulatory Compliance
In the highly regulated life sciences industry, SaaS solutions offer:
Automated documentation and reporting
Enhanced traceability and audit trails
Easier adherence to GxP guidelines
Cost-Effectiveness
SaaS models provide:
Reduced upfront capital expenditure
Scalable solutions that grow with the business
Lower maintenance and upgrade costs
Data-Driven Decision Making
SaaS platforms offer:
Advanced analytics capabilities
Real-time insights into manufacturing processes
Predictive modeling for process optimization
Overcoming Challenges in SaaS Adoption
While the benefits of SaaS in life science manufacturing are significant, organizations must address several challenges:
Data Security and Privacy
Life science companies deal with sensitive data. SaaS providers must demonstrate robust security measures, including:
End-to-end encryption
Compliance with data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA)
Regular security audits and certifications (e.g., ISO/IEC 27001, SOC 2 Type 2)
Integration with Existing Systems
Seamless integration with current manufacturing systems is crucial. Successful SaaS providers offer:
APIs and connectors for easy integration
Interoperability with existing workflows
Support for data migration and system transition
Regulatory Compliance
SaaS providers serving the life sciences industry must:
Understand and adhere to GxP regulations
Provide comprehensive documentation and validation support
Offer transparency in their quality management processes
Change Management
Transitioning to a SaaS model requires:
Employee training and upskilling
Cultural shifts towards digital-first mindsets
Clear communication of the benefits and processes involved
The Future of SaaS in Life Science Manufacturing
As SaaS continues to evolve, we can expect:
Increased AI and Machine Learning Integration: More sophisticated predictive analytics and autonomous decision-making in manufacturing processes.
Enhanced Collaboration: Cloud-based platforms facilitating seamless collaboration across global manufacturing sites.
Personalized Medicine Support: SaaS solutions enabling more agile manufacturing processes to support the growing trend of personalized therapeutics.
Blockchain Integration: Improved traceability and supply chain management through blockchain-enabled SaaS platforms.
Conclusion
Service as Software represents a paradigm shift in life science manufacturing, offering unprecedented opportunities for efficiency, quality, and innovation. As the industry continues to evolve, embracing SaaS will be crucial for organizations looking to stay competitive and deliver high-quality, safe, and effective products to patients.
The journey to becoming a successful SaaS provider in the life sciences industry requires a delicate balance of technological expertise and regulatory knowledge. Companies that can navigate this landscape effectively will be well-positioned to lead the next wave of innovation in life science manufacturing.
By leveraging the power of SaaS, life science manufacturers can not only streamline their operations but also accelerate the development and production of life-saving therapies, ultimately contributing to better patient outcomes and advancing global health.
Detailed Architecture of SaaS for GxP
A robust SaaS architecture for GxP compliance includes several critical components:
Data Management Layer
Data security, quality, and integrity are guaranteed by the data management layer. It has functions for gathering, storing, processing, and retrieving data together with thorough audit trails and validation procedures.
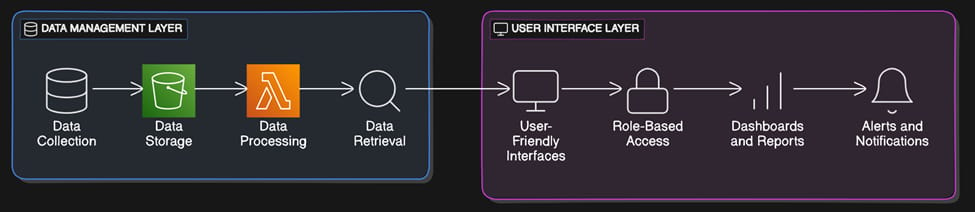
Data Collecting
Accurate and consistent data collecting is ensured by implementing standardized methods. This involves combining data from several sources and utilizing electronic data capture tools.
Data Storage
To preserve data integrity and guarantee that data is available when needed, secure and compliant data storage solutions are crucial. This entails putting disaster recovery, backup, and data encryption procedures into action.
Data Processing
Preserving the accuracy and efficiency of data processing is essential to data quality. To do this, procedures for data validation and cleaning that eliminate mistakes and inconsistencies must be put in place.
Data Retrieval
Ensuring that data is easily and securely accessible contributes to its ability to be retrieved when needed. This entails putting role-based access restrictions into place and making sure data retrieval procedures adhere to security specifications.
AI and Analytics Layer
Advanced analytics and machine learning capabilities are offered by the AI and analytics layer. By utilizing high-quality data, it permits anomaly identification, process improvement, and predictive modeling.
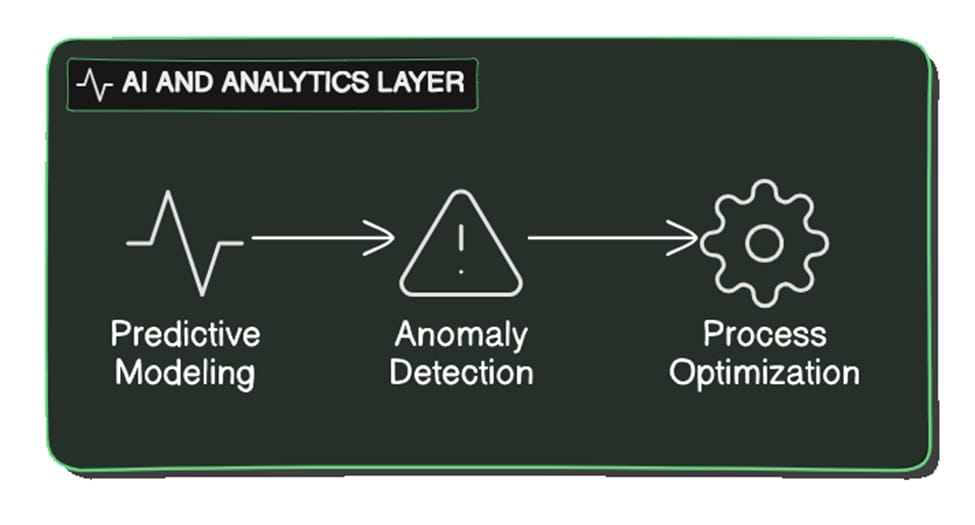
Predictive Modeling
Organizations can see patterns and make wise decisions by utilizing predictive modeling techniques. This involves predicting product quality, spotting any problems, and streamlining production processes with AI models.
Anomaly Detection
By putting anomaly detection tools in place, businesses may find any problems early on and take action before they become serious. This includes identifying possible quality problems and applying AI to find departures from typical trends.
Process Optimization
Organizations may increase productivity and cut expenses by utilizing AI and analytics to enhance manufacturing processes. This includes making adjustments to increase productivity and applying AI to find areas for process improvement.
Compliance Layer
The compliance layer makes sure that GxP standards are followed by integrating regulatory requirements into the system. It has electronic signing, reporting, and documentation facilities.
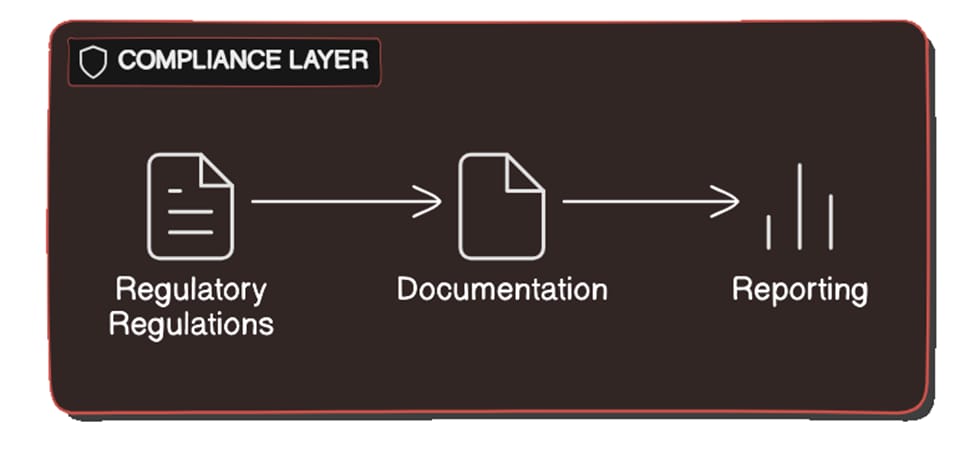
Regulatory Compliance
Maintaining GxP compliance depends on the SaaS solution's compliance with regulatory regulations. Putting in place mechanisms for electronic signatures, audit trails, and validation procedures is part of this.
Documentation
Having tools for documentation makes it easier to make sure that all required material is up to date and readily available. SOPs, validation procedures, and training materials fall under this category.
Reporting
Putting in place strong reporting capabilities makes sure that businesses can provide the reports required to prove they are in compliance with regulatory standards. Creating audit reports, quality reports, and regulatory submissions are all included in this.
User Interface Layer
User-friendly interfaces for accessing and engaging with the system are provided by the user interface layer. It offers dashboards, reports, and alerts along with support for multiple user roles.
User-Friendly Interfaces
Ensuring that users can access and interact with the system with ease is made possible by the provision of intuitive and user-friendly interfaces. This involves creating user-friendly and intuitive interfaces.
Role-Based Access
By putting role-based access controls in place, you can make sure that users can only access the information and features they require. This involves assigning user roles and permissions in accordance with the duties and obligations of their jobs.
Dashboards and Reports
Giving users access to dashboards and reports facilitates their understanding of the data. This entails creating reports that offer insights into important metrics and performance indicators as well as putting in place configurable dashboards.
Alerts and Notifications
Setting up alerts and notifications makes sure people are aware of important problems and can respond appropriately. This involves creating alerts for abnormalities, deviations, and other noteworthy occurrences.
Integration Layer
The smooth integration of new systems and procedures is guaranteed by the integration layer. For integrating with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS), and other vital applications, it must have connectors and APIs.
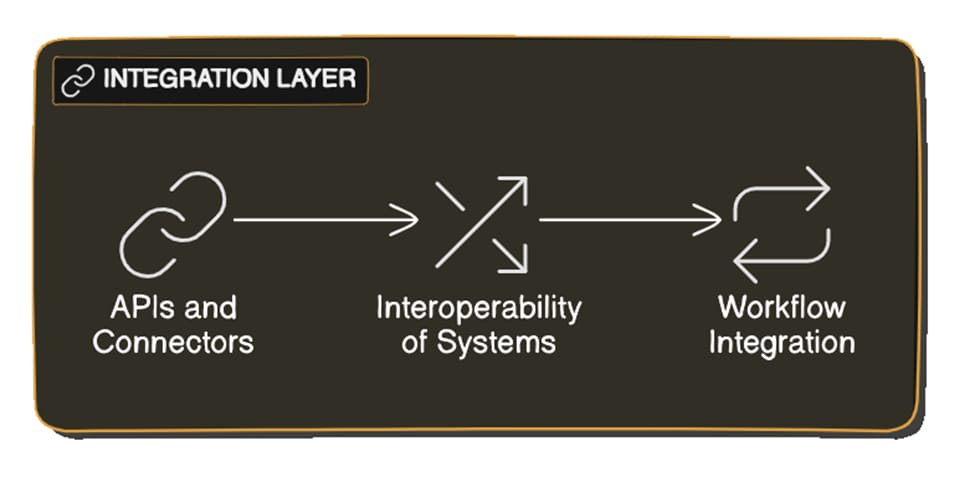
APIs and Connectors
Putting APIs and connectors in place makes it more likely that the SaaS solution will function with current workflows and systems. Creating and managing APIs for data interchange and application integration falls under this category.
Interoperability of Systems
Securing interoperability between the SaaS solution and other systems aids in maintaining data consistency and optimizing workflows. This entails putting data interchange standards into practice and making sure different systems work together.
Workflow Integration
Making sure the SaaS solution can be easily integrated into regular operations is ensured by integrating it with current workflows. This entails creating procedures for data sharing and cooperation as well as specifying integration points.

