Credits: Stability.AI
Table of Contents
Introduction
Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) are essential in the pharmaceutical and life sciences industries for managing laboratory data and adhering to regulatory standards. These systems streamline operations, improve data integrity, and ensure compliance through effective data tracking.
This case study focuses on xLM Continuous Validation, emphasizing Baseline Validation and Requalification. Continuous validation enables organizations to monitor their Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) effectively. Baseline validation sets a performance and compliance standard, while Requalification maintains the validated status over time. The study showcases the advantages of xLM Continuous Validation, showcasing improvements in data integrity, risk management, and operational efficiency.
Background
LIMS Systems are software solutions that assist laboratories in managing samples, associated data, and laboratory workflows. They play a crucial role in upholding the quality and integrity of laboratory processes, particularly in regulated environments like pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and clinical research.
Key Functions of LIMS
Sample Management: LIMS offer tools for monitoring samples from collection to analysis and storage, ensuring accurate and easily accessible data for each sample.
Data Integrity: Through automated data collection and analysis, LIMS reduce human error and improve the reliability of laboratory results, crucial for adhering to Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
Regulatory Compliance: LIMS are tailored to assist laboratories in meeting various regulations, including FDA 21 CFR Part 11, which regulates electronic records and signatures, ensuring trustworthy and validated laboratory data.
Workflow Automation: LIMS streamline laboratory workflows by automating tasks like data entry, reporting, and inventory management, enabling staff to focus on more intricate analytical duties.
Reporting and Analytics: LIMS offer robust reporting tools for generating compliance reports, analyzing data trends, and facilitating decision-making processes.
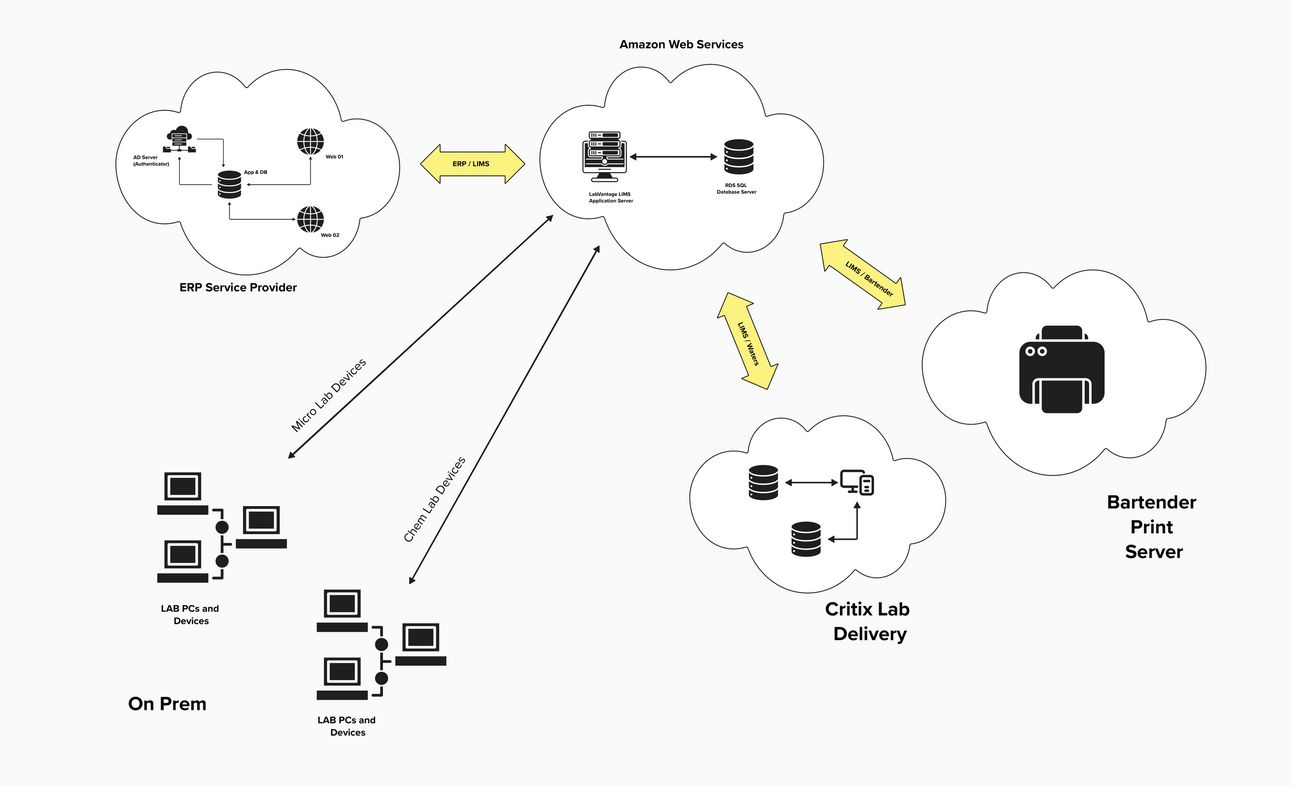
Network Architecture (High Level)
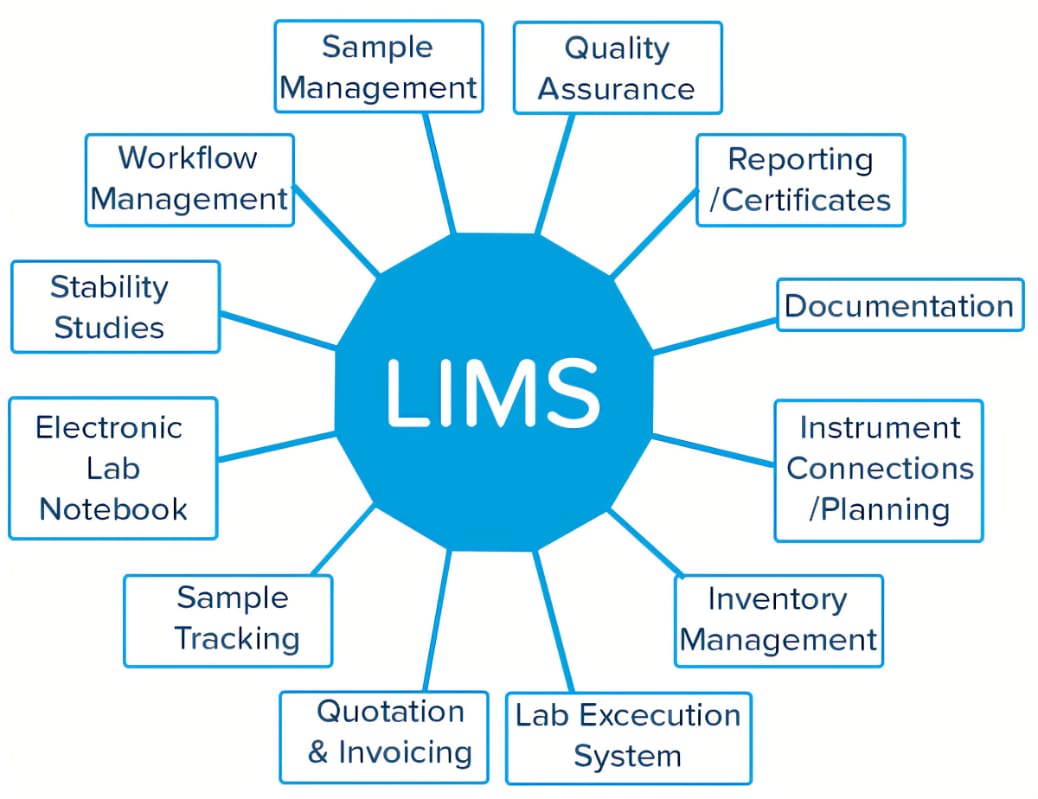
LIMS Functional Areas
Common Challenges
Validating LIMS in the pharmaceutical and medical device industries involves addressing key challenges for compliance and data integrity. Challenges include validating raw materials from multiple suppliers, establishing testing methods, and specifications. Qualifying finished instruments, ensuring proper installation, and operational qualification is crucial, along with maintaining data integrity.
Stability programs require designing studies for storage conditions, analyzing trends, and ensuring representative samples. Validating finished product workflows involves managing sample, test execution, and reporting complexities, ensuring consistency, and maintaining a validated LIMS state.
Proactive risk assessment, robust documentation, monitoring, and continuous improvement are essential for data integrity and compliance.
Solutions and Implementation - Continuous Validation
Validation Approach
The approach for the LIMS System focused on ensuring the system meets regulatory requirements and user needs through a structured validation plan. This includes validating key functionalities such as stability study management, batch and sample management for finished goods and raw materials, quality control batching, consumable tracking, and the creation of barcoded labels.
Additionally, the validation process encompasses interfaces with existing systems, including the ERP system and Chromatography Data System (CDS).
User Requirement Specification
The User Requirement Specification (URS) for the LIMS delineates the crucial user requirements essential for achieving the system's objectives. It focuses on functionalities like sample test data entry, batch creation and disposition, consumable lot management, stability sample studies, ERP integration, instrument data collection, and label printing.
The process of finalizing these requirements followed a Continuous Application Lifecycle Management (cALM) approach. This approach involved collaboratively developing and refining infrastructure, integration, and business process requirements.
All the requirements were efficiently managed using ContinuousALM app.
This systematic method ensured the accurate capture and documentation of all user requirements, establishing a clear framework for LIMS implementation that aligned with business processes such as quality control management, stability study management, and custom Certificate of Analysis (COA) reporting.
Functional Design Specification
The Functional Design Specification (FDS) delineated the functional requirements and detailed design specifications to effectively support users at the multiple facilities. The FDS was created by developing interface specifications, installation, and operation specifications.
Design Specifications were again managed effectively in ContinuousALM that has a built-in support for bi-directional traceability
Configuration Qualification
The purpose of this Configuration Qualification (CQ) was to provide documented evidence that the LIMS System was configured to meet the requirements and specifications. This CQ document focused on verifying specific LIMS configuration settings, including security parameters, user roles, password validation, job types, system configuration, and monitoring policies.
Additionally, it encompasses the verification of log file viewers, reporting capabilities, label methods, and instrument protocols. By systematically validating these configuration settings, the protocol ensured that the LIMS functioned as intended, thereby supporting reliable laboratory operations and compliance with regulatory standards.

ContinuousALM - Configuration Qualification
Risk Assessment
The Risk Assessment (RA) wss designed to identify and prioritize the highest-risk functions within the system. This assessment provided a structured justification for which components of the LIMS would undergo testing based on a thorough risk analysis, guiding the overall testing efforts.
Central to this process was the Risk Priority Number (RPN), which was calculated by evaluating the occurrence, severity, and detection ratings of potential risks. Items deemed low-risk would not require additional testing, as they have already been thoroughly evaluated during system development and release. By focusing on high-risk areas, the RA served as a critical tool for ensuring that the LIMS implementation was both efficient and compliant, ultimately enhancing the reliability of laboratory operations.
Risk Management leveraged the built-in ContinuousALM feature, thus providing an efficient framework to manage risk.
Validation Testing and Test Automation
Testing is a critical aspect of the validation process involving the development of detailed test cases categorized into Installation Qualifications (IQ), Operational Qualifications (OQ), and Performance Qualifications (PQ).
By leveraging the xLM inbuilt framework for test automation, we efficiently executed complex scenarios without manual intervention, ensuring robust testing of workflows for Finished Products, Finished Instruments, Raw Materials, Consumables, and Stability studies.
Key functionalities, such as reporting, navigating the directories to access files, updating sample fields with generated sample IDs, and verifying audit trails, were seamlessly integrated into the automated testing process.
The segregation of test data from scripts enhanced reusability and simplified maintenance, as only impacted variables needed updating during testing. Furthermore, the modular structure of the framework, combined with data-driven testing and integration with xLM's CI/CD tools, enabled the automation of testing pipelines. This resulted in the generation of auto-generated test reports through a our PDF reporting services. This comprehensive approach not only optimized testing efficiency but also ensures thorough validation of the LIMS System functionaly.
The matrix below illustrates the execution time of the automation run compared to manual execution.
Sr # | Workflow Name | Automation Execution (Sequential) (In Hours) | If executed Manually (In Hours) |
1 | Raw Materials Workflow | 0.5 | 8 |
2 | Consumable Workflow | 0.5 | 11 |
3 | Finished Products and Instruments Workflow | 1.5 | 15 |
4 | Stability Workflow | 1.25 | 14 |
| Total | 3.75 | 47 |
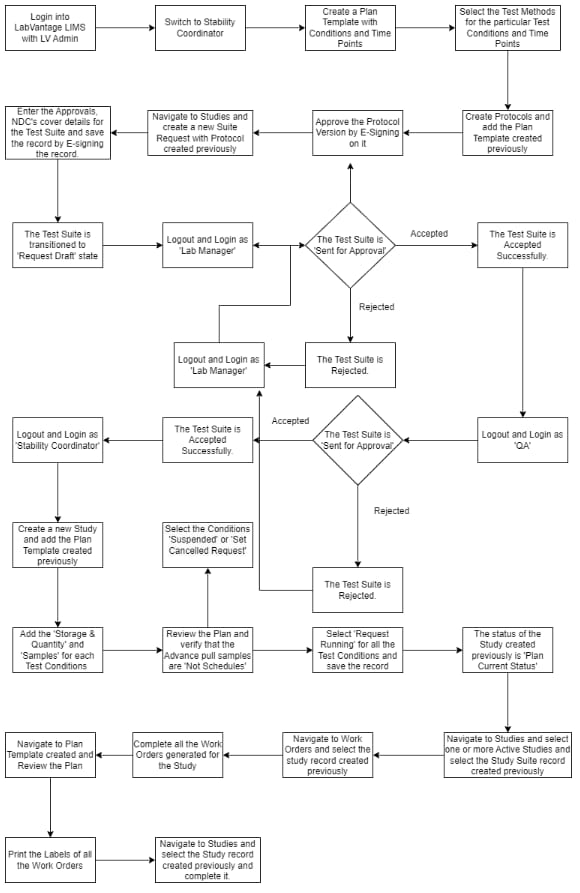
Sample Workflow: Stability

ContinuousALM - Operational Qualification
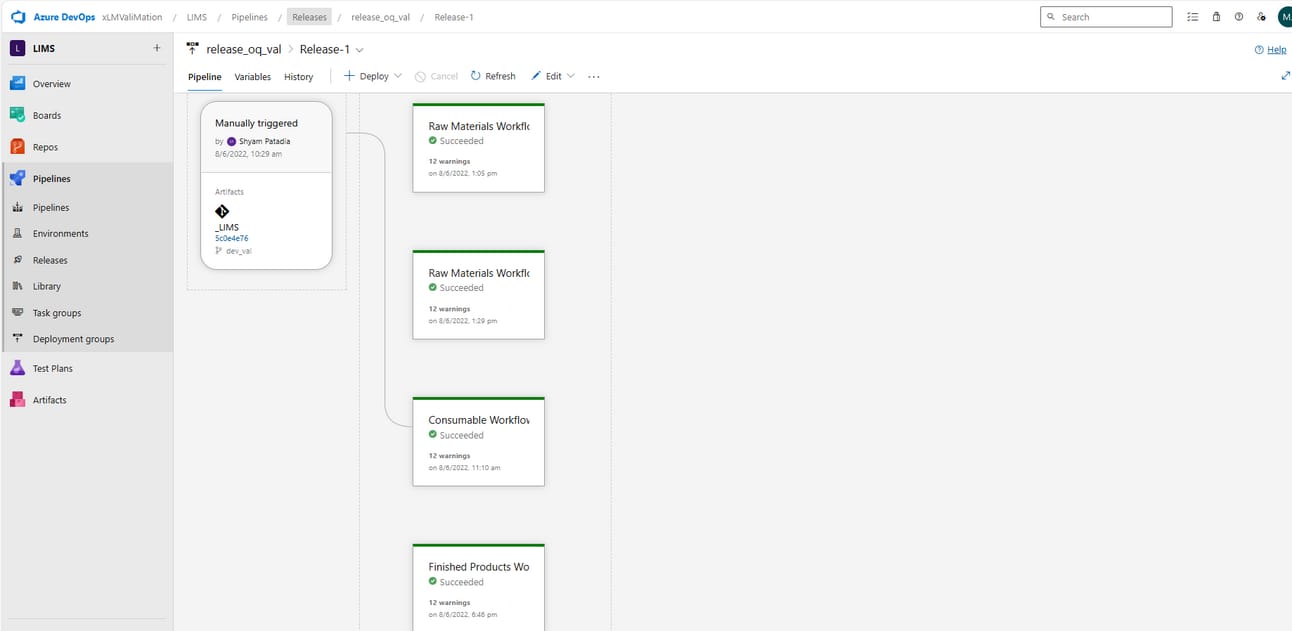
CI/CD Pipeline with successful Run

Audit Trail of a successful CI/CD stage
Traceability Matrix
Bi-directional traceability is built into ContinuousALM. Managing the relationships between requirements > specifications > test cases is a cinch.
Validation Summary Report
Once a particular validation run is completed, xLM’s QA authored the Summary Report and ensured that all the approved artifacts were posted to the Customer Portal.
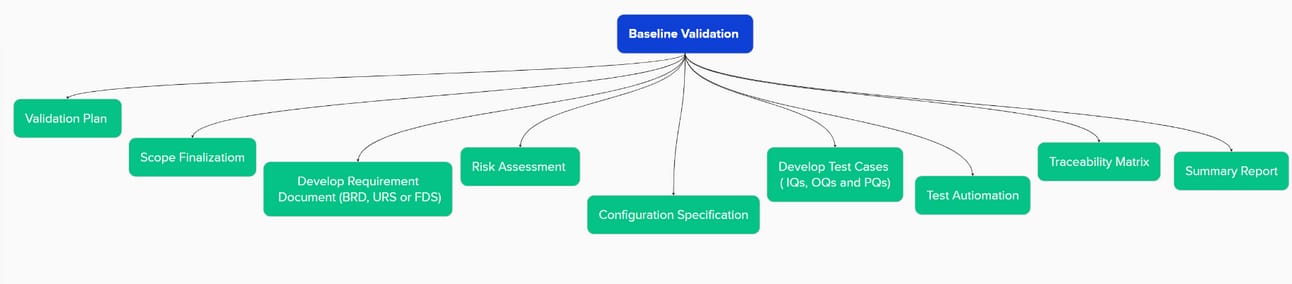
xLM Continuous Validation - Baseline Validation
Conclusion
The xLM Continuous Validation approach for the LIMS System proved highly effective in enhancing data integrity, managing risks, and ensuring operational efficiency.
The robust framework of Baseline Validation and Periodic Requalification ensures continuous compliance with regulatory standards.
xLM Continuous Validation is a far superior solution in the industry where every aspect of a complex LIMS can be validated including interfaces to ERP, Lab CDMS, Label Printing Systems, etc..
The test coverage is at a minimum 10x as compared to conventional manual methods.
The speed of testing is unmatched by manual methods.
100% regression testing with every patch and release is only made possible by our platform.
All these superior features are delivered at half the cost.


